
Creating partitions
Now you should plan the layout of your hard disk partitionsregarding file system and size. I recommend creating three or fourpartitions in addition to the Windows partition. The following exampleassumes you have exactly one Windows partition (drive letter C). Yourhard disk would then look like this:
First partition: NTFS or FAT32 (Windows)
Second partition: ext2 or ext3 (this is where Puppy will be installied to)
Third partition: Linux swap (for page files)
Fourth partition: FAT32 (for exchanging data between Windows and Linux)
Optionally, a fifth partition: ext2 or ext3 (Linux)
Windows will continue to reside on your first partition with all itsprograms and data. The second partition (recommended size about 1-2 GB)has a Linux file system (ext2 or ext3). This is the partition Puppywill be installed to. The third partition (exactly as large as yourcomputer's memory) will be a Linux swap partition that Linux can ...well, swap files to. The fourth partition has a FAT32 file system,which is recognized by both Windows and Linux. This partition(recommended size about 5 GB) is used for files that you want to accessfrom both Windows and Linux. If you want to manage large amounts ofdata under Puppy (e.g. music collection, pictures), you should create afifth partition with a Linux file system (ext2/ext3). This file systemcannot be accessed from Windows and is meant for Linux only.
To create the partitions, proceed as follows:
Start Puppy Linux from CD with the "pfix=ram" boot option.
Start the Gparted program: "Menu | System | Gparted partition manager".
First, shrink your Windows partition (NTFS file system). To do this, select the Windows partition /dev/hda1.
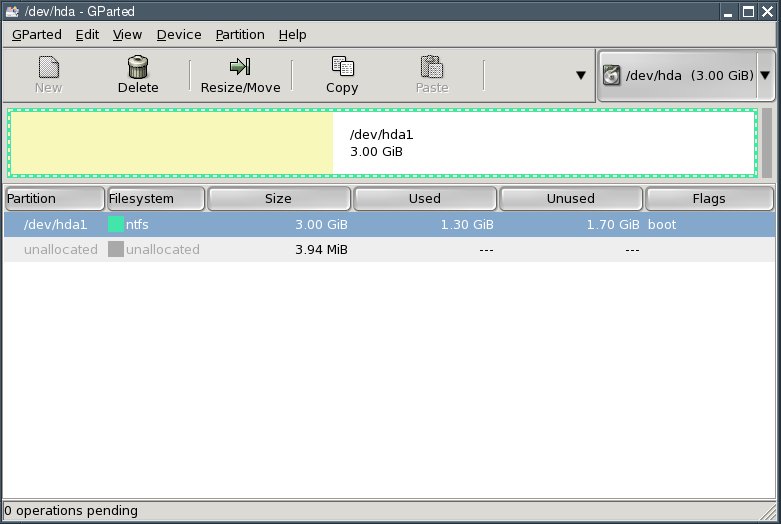
Click the "Resize/Move" button.
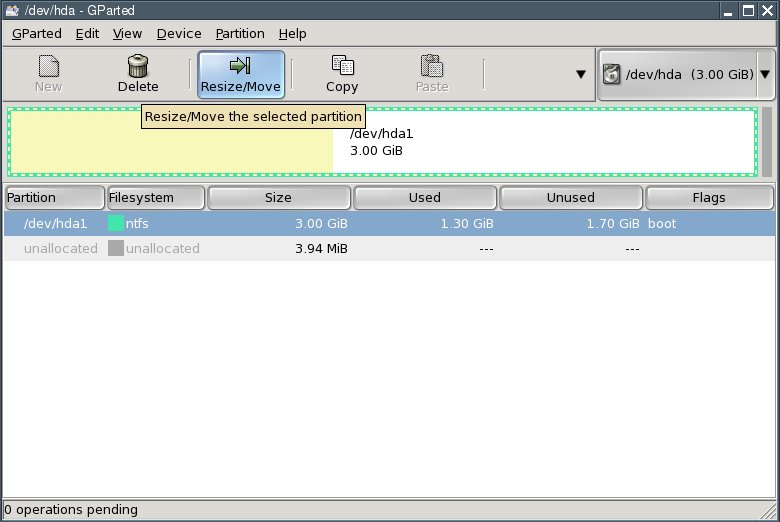
Reduce the "New Size" value until the "Free Space Following" fieldshows enough free space following for the new partitions. My testcomputer's hard disk has only 3 gigabytes; I am using half of that forthe mew partitions. You probably have a much larger hard drive so yourpartition sizes can be increased accordingly.
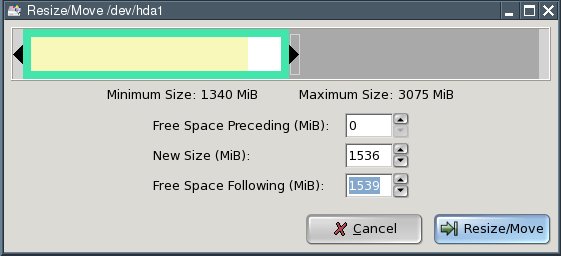
Then press the "Resize/Move" button.
Next, select "Edit | Apply All Operations" from the menu.
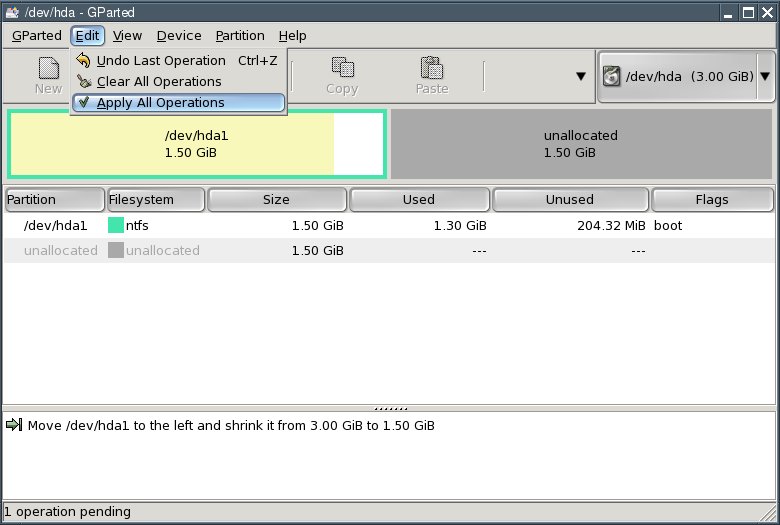
In the dialogue box that comes up, click the "Apply" button.
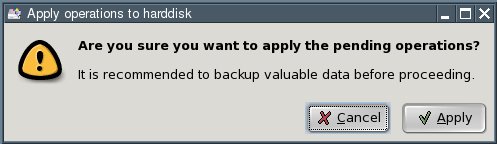
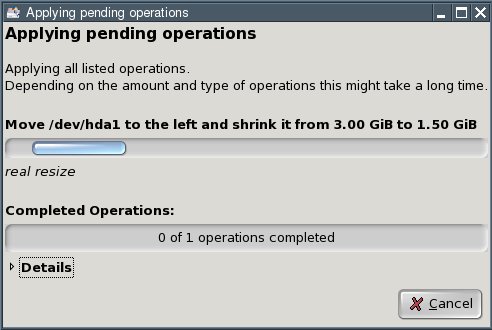
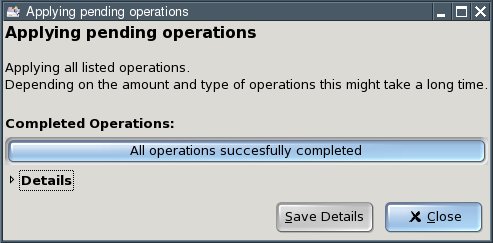
Click the "Close" button. You now have an "unallocated" area on your hard disk.
Select the line saying "unallocated" and click the "New" button.
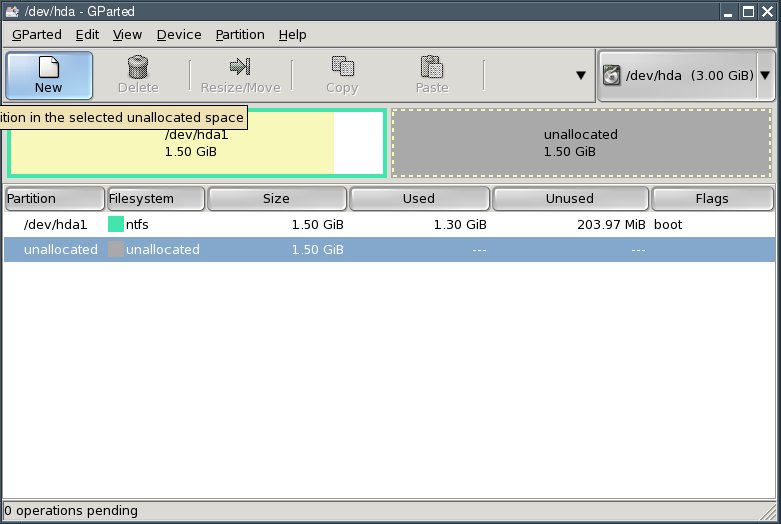
Enter the size of the second partition in the "New Size" field. Thisis where Puppy Linux will be installed to. I recommend a size of 1 to 2gigabytes (i.e., 1024 to 2048 MB). Select ext2 from the "Filesystem"box and click "Add".

Again select the line saying "unallocated" and click the "New" button. (You can see where this is going.)

Enter the size of the third partition in the "New Size" field. Thispartition is to hold Linux's swap files as a Linux swap partition. Youshould make it as large as your computer's memory (RAM). With my testcomputer, this amounts to 128 megabytes (MB). Select linux-swap fromthe "Filesystem" box and click "Add".
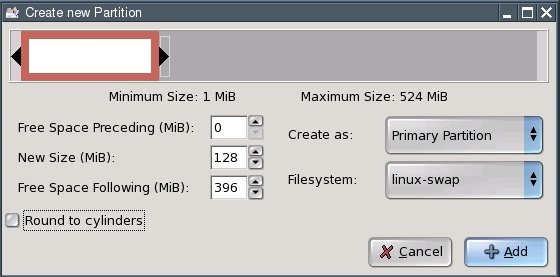
Again select the line saying "unallocated" and click the "New" button.

Enter the size of the fourth partition in the "New Size" field.Thispartition is meant for shared access to files from Windows and Linux. Irecommend a size of about 5 gigabytes (5120 MB). Since my test computerdoes not have a large enough hard disk, I am using 396 megabytes (MB)as an example. Select FAT32 from the "Filesystem" box and click "Add".
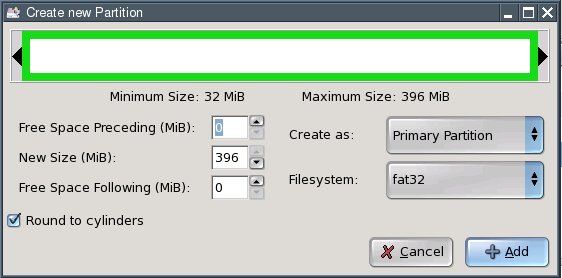
Hint: if you want to create additional partitions (e.g., for verylarge files under Linux), repeat the process outlined aboveaccordingly. In this case, you may have to create so-called logicalpartitions. Please consult additional sources if you are unsure abouthow to do that.
To actually write the changes to disk, select "Edit | Apply All Operations" from the menu.
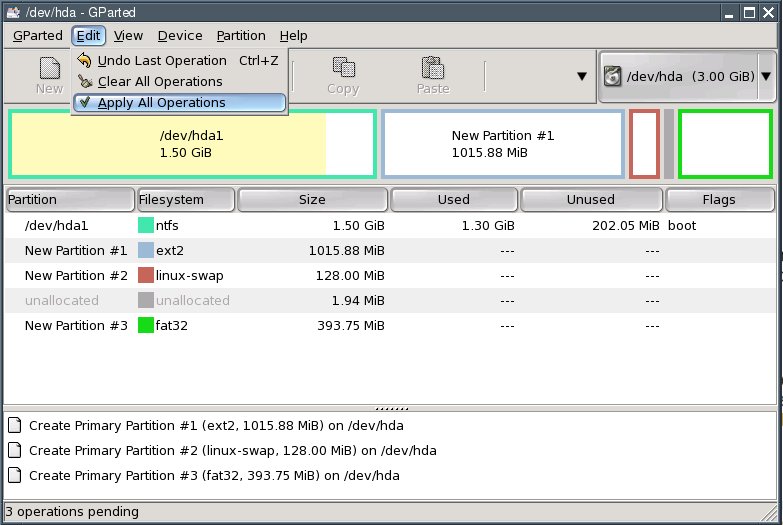
In the dialogue box that comes up, click "Apply".


Click the "Close" button.
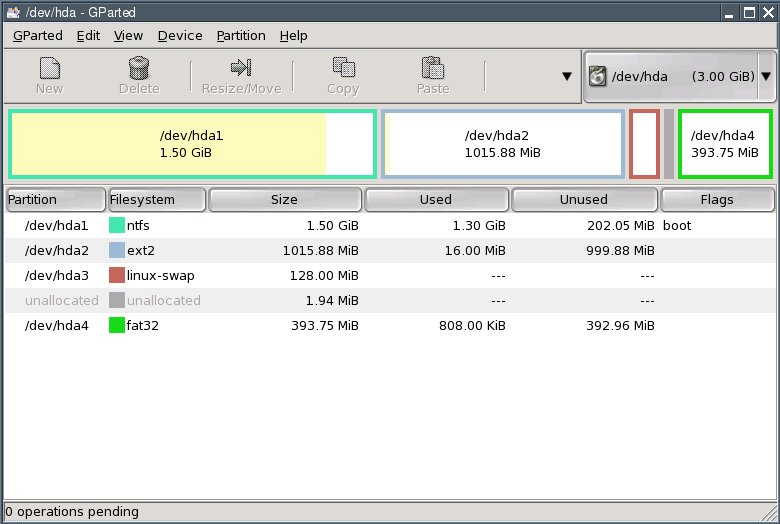
Exit GParted.
Now you should plan the layout of your hard disk partitionsregarding file system and size. I recommend creating three or fourpartitions in addition to the Windows partition. The following exampleassumes you have exactly one Windows partition (drive letter C). Yourhard disk would then look like this:
First partition: NTFS or FAT32 (Windows)
Second partition: ext2 or ext3 (this is where Puppy will be installied to)
Third partition: Linux swap (for page files)
Fourth partition: FAT32 (for exchanging data between Windows and Linux)
Optionally, a fifth partition: ext2 or ext3 (Linux)
Windows will continue to reside on your first partition with all itsprograms and data. The second partition (recommended size about 1-2 GB)has a Linux file system (ext2 or ext3). This is the partition Puppywill be installed to. The third partition (exactly as large as yourcomputer's memory) will be a Linux swap partition that Linux can ...well, swap files to. The fourth partition has a FAT32 file system,which is recognized by both Windows and Linux. This partition(recommended size about 5 GB) is used for files that you want to accessfrom both Windows and Linux. If you want to manage large amounts ofdata under Puppy (e.g. music collection, pictures), you should create afifth partition with a Linux file system (ext2/ext3). This file systemcannot be accessed from Windows and is meant for Linux only.
To create the partitions, proceed as follows:
Start Puppy Linux from CD with the "pfix=ram" boot option.
Start the Gparted program: "Menu | System | Gparted partition manager".
First, shrink your Windows partition (NTFS file system). To do this, select the Windows partition /dev/hda1.

Click the "Resize/Move" button.

Reduce the "New Size" value until the "Free Space Following" fieldshows enough free space following for the new partitions. My testcomputer's hard disk has only 3 gigabytes; I am using half of that forthe mew partitions. You probably have a much larger hard drive so yourpartition sizes can be increased accordingly.

Then press the "Resize/Move" button.
Next, select "Edit | Apply All Operations" from the menu.

In the dialogue box that comes up, click the "Apply" button.



Click the "Close" button. You now have an "unallocated" area on your hard disk.
Select the line saying "unallocated" and click the "New" button.

Enter the size of the second partition in the "New Size" field. Thisis where Puppy Linux will be installed to. I recommend a size of 1 to 2gigabytes (i.e., 1024 to 2048 MB). Select ext2 from the "Filesystem"box and click "Add".

Again select the line saying "unallocated" and click the "New" button. (You can see where this is going.)

Enter the size of the third partition in the "New Size" field. Thispartition is to hold Linux's swap files as a Linux swap partition. Youshould make it as large as your computer's memory (RAM). With my testcomputer, this amounts to 128 megabytes (MB). Select linux-swap fromthe "Filesystem" box and click "Add".

Again select the line saying "unallocated" and click the "New" button.

Enter the size of the fourth partition in the "New Size" field.Thispartition is meant for shared access to files from Windows and Linux. Irecommend a size of about 5 gigabytes (5120 MB). Since my test computerdoes not have a large enough hard disk, I am using 396 megabytes (MB)as an example. Select FAT32 from the "Filesystem" box and click "Add".

Hint: if you want to create additional partitions (e.g., for verylarge files under Linux), repeat the process outlined aboveaccordingly. In this case, you may have to create so-called logicalpartitions. Please consult additional sources if you are unsure abouthow to do that.
To actually write the changes to disk, select "Edit | Apply All Operations" from the menu.

In the dialogue box that comes up, click "Apply".


Click the "Close" button.

Exit GParted.
- 适合打印的版本
- 13051 次点击

,现在你应该计划您的硬盘partitionsregarding文件系统和大小的布局。我建议创建Windows分区中的三个或 fourpartitions。以下exampleassumes你有一个Windows分区(驱动器号C)。Yourhard磁盘,然后看起来像这样:
第一分区:NTFS或FAT32(Windows)中
的第二个分区:ext2或ext3(这是小狗将被installied)
第三个分区:Linux交换(页面文件)
第四个分区:FAT32(交换Windows和Linux)之间的
数据(可选),第五个分区:ext2或ext3(Linux)
的视窗将继续驻留在你的第一个分区的所有itsprograms和数据。第二个分区(推荐的约1-2 GB的大小)一个Linux文件系统(ext2或ext3) 。这是安装到分区Puppywill。第三个分区(完全yourcomputer的内存一样大),将一个Linux交换分区,Linux可以...好,交换文件。第四个分区FAT32文件系统,这是由Windows和Linux的认可 。这个分区(推荐大小约5 GB)用于要accessfrom Windows和Linux的文件 。如果你想ofdata大量管理下的小狗(如音乐收藏,照片),你应该创建一个Linux文件系统(ext2/ext3的)afifth分区。这个文件systemcannot访问从Windows,只是为Linux。
创建分区,步骤如下:
从光盘启动“pfix = RAM”引导选项的Puppy Linux。
开始的gparted方案:“菜单|系统|的gparted分区经理“。
第一,收缩你的Windows分区(NTFS文件系统)。要做到这一点,选择Windows分区/ dev/hda1 ,点击“调整大小/ 移动,直到“自由空间之后”fieldshows足够的自由空间,新的分区,减少“大小” 值 “按钮。。我testcomputer的硬盘只有3千兆字节,我使用该forthe MEW分区的一半 。你可能有一个更大的硬盘驱动器,可相应增加,使 yourpartition大小,然后按“调整大小/移动 “按钮。下一步,选择”编辑“|”应用所有 操作“,从菜单中出现的对话方块中,单击“Apply”按钮 ,单击“关闭”按钮 。现在,您可以 选择一个硬盘上的“未分配”的区域。行,说“未分配”,然后单击“新建” 按钮。输入“新建大小”字段中的第二个分区的大小。Thisis其中的Puppy Linux将安装到。我建议的大小为1 2gigabytes(即1024到2048 MB)。从“文件系统”框中选择ext2和点击“添加” ,再次选择行说:“未分配”,然后单击“新建”按钮 。(你可以看到这是怎么回事。) 进入“新建大小”字段中的第三个分区的大小。Thispartition是保持Linux的交换文件,作为一个Linux交换分区 。Youshould使您的计算机的内存(RAM)大。随着我testcomputer,这相当于128兆字节(MB)。选择Linux的交换fromthe“文件系统”框中,单击“添加”。 再次选择行说:“未分配”,然后单击“新建”按钮。 ,输入在“新尺寸”field.Thispartition的第四个分区的大小是Windows和Linux中的文件进行共享访问。Irecommend一个大约5千兆字节(5120 MB)的大小。由于我的测试computerdoes没有一个足够大的硬盘,我使用396兆字节(MB)作为一个例子。FAT32和选择“文件系统”框中单击“添加”。 提示:如果你要创建其他分区(例如,对于verylarge Linux下的文件),重复这个过程概述aboveaccordingly 。在这种情况下,您可能必须建立所谓的logicalpartitions。请咨询其他来源,如果您不确定abouthow做 ,要真正写入到磁盘的更改,选择“编辑|应用所有操作 “菜单,在出现的对话方块中,点击 “应用” ,点击“关闭“按钮, 退出的gparted。
发表新评论